Boolean operators produce a single boolean output value from one or more input values. There are three boolean operators in boolean algebra: AND, OR, and NOT. Python uses and, or, and not to implement them. We shall learn about Python’s not operator in this tutorial.
The not operator
It is used to get the negation of a value, i.e. it allows us to invert the truth value of a given boolean expression. This operator can be applied in boolean situations like if statements and while loops. It also functions in non-Boolean settings, enabling you to reverse the variables’ truth values.
The below table shows the outcomes for some input values when the not the operator is applied to them.
| Input | Output |
| True | False |
| False | True |
not is a unary operator which means it takes only one input value. It can be used with any boolean expression or Python object.
Using not with different data types
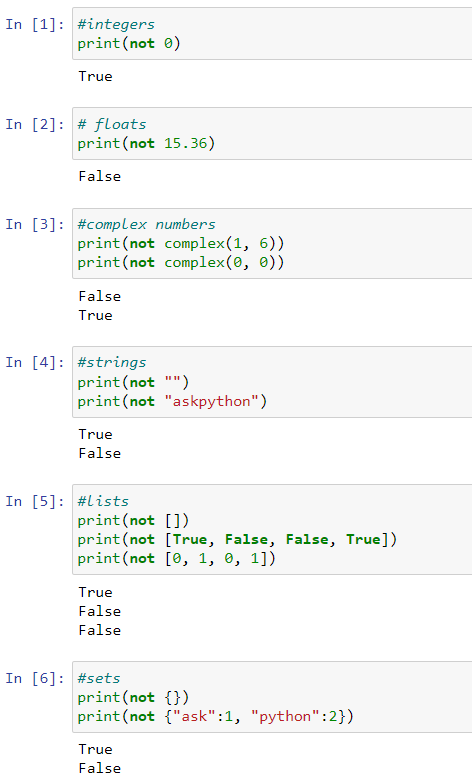
not with Different Data TypesUsing not with conditional statements
Let’s see how the not operator in Python works with the different types of conditional statements we have.
if statement
num = 25
if not num%2==0:
print("num is an odd number")
else:
print("num is an even number")
Output:
num is an odd number
Here, num%2 i.e. 25%2 equals 1 and not 0. The if statement checks whether num%2==0 is False. Since the condition is satisfied, the output says the number is odd. If it were an even number, the else condition would have been satisfied.
while loop
count = 1
while not count>5:
print(count)
count = count + 1
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
The condition count>5 checks if the number of records is greater than 5. The while loop executes till count is less than 5. Once count‘s value becomes 6, the loop will terminate.
Methods of implementing the not boolean operator in Python
Method 1: Using the ‘not’ keyword
var = False
print(not var)
Output:
True
var = True
print(not var)
Output:
False
Above are simple examples of using the not keyword in Python.
Method 2: Using the ‘~’ operator
‘~’ is called the negation operator.
flag = True
print("Flag is ", flag)
print("Flag is ", bool(~flag))
Output:
Flag is True
Flag is False
In this example, the flag is set to True at first and its value is printed. In the next line, we first take the negation of flag by writing ~flag and we have written bool(~flag) because if the flag was not a boolean at first, then it will be converted into a boolean.
Method 3: Using the operator module
The operator module in Python provides various methods like addition, subtraction, exponentiation, left shift, right shift, etc. One among these many methods is not_(). It returns the negated value of the argument provided to it.
import operator
initial_list = [False, True, True, False]
print("Initial list:", initial_list)
negated_list = []
for i in range(0, len(initial_list)):
negated_list.append(operator.not_(initial_list[i]))
print("Negated list:", negated_list)
Output:
Initial list: [False, True, True, False]
Negated list: [True, False, False, True]
Here, we have first imported the operator module. Then we created a list of some boolean values. The loop iterates over the ‘initial_list’ and negates each value using the not_() method from the operator module and appends it to the ‘negated_list’.
Method 4: Using the bitwise_not() method from NumPy
Numpy provides a bitwise_not() method to find the negation of a value. It performs bitwise NOT operation on its arguments.
import numpy as np
print(np.bitwise_not(True))
print(np.bitwise_not(False))
Output:
False
True
The above code uses the bitwise_not() method to negate only a single value. We can also use a NumPy array of elements as shown below.
import numpy as np
a = np.array([True, False, False])
a = np.bitwise_not(a)
print(a)
Output:
[False True True]
Method 5: Using the invert() method from NumPy
This method also performs the bitwise NOT operation on arguments passed to it. It can be used on a single element or an array of elements.
import numpy as np
print(np.invert(False))
print(np.invert(True))
Output:
True False
Another example:
import numpy as np
a = [True, False, False]
a = np.invert(a)
print(a)
Output:
[False True True]
Method 6: Using the logical_not() method from NumPy
This method can also be used for finding the negation of a boolean value. Just like the bitwise_not() and invert() methods, this method can also be applied to both, a single argument or a list of arguments as shown below.
import numpy as np
print(np.logical_not(False))
print(np.logical_not(True))
Output:
True
False
Another example:
import numpy as np
a = [True, False, True]
a = np.logical_not(a)
print(a)
Output:
[False True False]
Conclusion
That’s all! We have learnt about the not operator and also the different ways in which we can use it in Python.



