Python sys module deals with the system and environment-specific variables and parameters. We can use it to read the PATH variable and the list of command-line parameters passed to the Python script.
Import sys Module in Python
Before using any module, it needs to be imported.
Syntax:
import module_name
Example:
import sys
Python sys.modules
This variable let us know about the existing modules present or imported by the current shell.
Syntax:
>>> sys.modules.keys()
dict_keys(['sys', 'builtins', '_frozen_importlib', '_imp', '_thread', '_warnings', '_weakref', 'zipimport', '_frozen_importlib_external', '_io', 'marshal', 'posix', 'encodings', 'codecs', '_codecs', 'encodings.aliases', 'encodings.utf_8', '_signal', '__main__', 'encodings.latin_1', 'io', 'abc', '_abc', 'site', 'os', 'stat', '_stat', 'posixpath', 'genericpath', 'os.path', '_collections_abc', '_sitebuiltins', '_bootlocale', '_locale', 'types', 'importlib', 'importlib._bootstrap', 'importlib._bootstrap_external', 'warnings', 'importlib.util', 'importlib.abc', 'importlib.machinery', 'contextlib', 'collections', 'operator', '_operator', 'keyword', 'heapq', '_heapq', 'itertools', 'reprlib', '_collections', 'functools', '_functools', 'mpl_toolkits', 'readline', 'atexit', 'rlcompleter'])
>>>
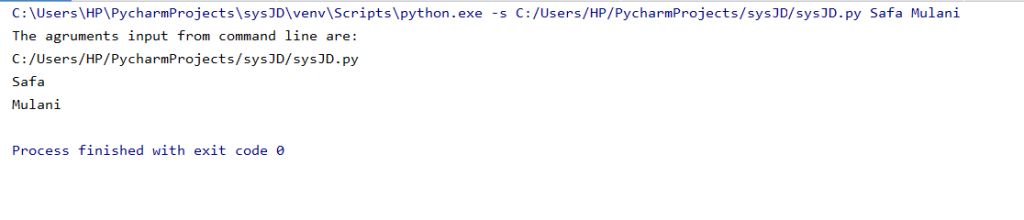
Python sys.argv
This gives us a list of command-line arguments passed to the python script
Example 1:
import sys
print('The agruments input from command line are:')
for x in sys.argv:
print(x)
Output:
Python sys.path
This variable displays the PATH of the current system or environment.
Syntax:
sys.path
Example:
import sys
sys.path
['', 'C:\Users\HP\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38-32\python38.zip', 'C:\Users\HP\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38-32\DLLs', 'C:\Users\HP\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38-32\lib', 'C:\Users\HP\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38-32', 'C:\Users\HP\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38-32\lib\site-packages']
Python sys.stdin
This function of sys module is used to accept input for a user-input-prompt program.
Syntax:
sys.stdin.readline()
Example:
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline()
print("Input : " + input)
Output:

As mentioned, the above example accepts input from the user and displays it.
Python sys.maxsize
This variable returns the largest integer value a variable can take and store.
Syntax:
sys.maxsize
Example:
import sys
sys.maxsize
Output:

Python sys.copyright
This variable displays the copyright of the current version of Python installed on the system.
Syntax:
sys.copyright
Example:
import sys
print(sys.copyright)
Output:

Python sys.getrefcount
This function of the sys module returns the count of references to the particular object being used within the particular piece of the code block.
Example:
import sys
input = "Engineering"
print(sys.getrefcount(0))
print(sys.getrefcount(input))
print(sys.getrefcount(None))
Output:

Python sys.exit
This function of sys module makes the Python interpreter end the execution of the current program abruptly. It is used to exit the program from the particular flow of control of the code.
Syntax:
sys.exit()
Example:
import sys
print("Engineering")
sys.exit(1)
print("Discipline")
Output:
Engineering
In the above example, as soon as the exit() function is encountered, it comes out of the execution of the particular program. Thus, “Discipline” doesn’t get printed in the output.
References
- Python sys module
- Python sys module Docs


