Array is basically a data structure that stores data in a linear fashion. There is no exclusive array object in Python because the user can perform all the operations of an array using a list.
So, Python does all the array related operations using the list object. The array is an ordered collection of elements in a sequential manner.
Syntax to declare an array:
array-name = []
Two-dimensional arrays are basically array within arrays. Here, the position of a data item is accessed by using two indices. It is represented as a table of rows and columns of data items.
Declaration of a 2-D Array
Syntax:
array-name = [ [d1, d2, .... dn], [e1, e2, .... en] ]
Example:
array_input = [ [10,12,14] ,[0,1,2] ]
print(array_input[0]) # printing elements of row 0
print(array_input[1]) # printing elements of row 1
Output:

Input to a 2-D Array
Input to a 2-D array is provided in the form of rows and columns.
Example:
size = int(input())
array_input = []
for x in range(size):
array_input.append([int(y) for y in input().split()])
print(array_input)
Output:

How to Insert elements in a 2-D array?
Elements in a 2D array can be inserted using the insert() function specifying the index/position of the element to be inserted.
from array import *
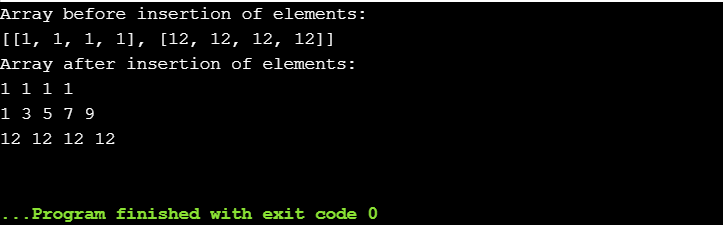
input = [[1,1,1,1], [12,12,12,12]]
print("Array before insertion of elements: ")
print(input)
input.insert(1, [1,3,5,7,9])
print("Array after insertion of elements: ")
for x in input:
for y in x:
print(y,end = " ")
print()
Output:
How to Update elements in a 2-D array?
The elements can be updated and the values can be changed by reassigning the values using the index of the array.
from array import *
input = [[1,1,1,1], [12,12,12,12]]
print("Array before Updation of elements: ")
print(input)
input[0] = [10,8]
input[1][1] = 9
print("Array after updation of elements: ")
for x in input:
for y in x:
print(y,end = " ")
print()
Output:

How to Delete values from a 2-D array?
The elements from a 2-D array can be deleted using del() method.
from array import *
input = [[1,1,1,1], [12,12,12,12], [0,2]]
print("Array before Deletion of elements: ")
print(input)
del(input[1])
print("Array after Deletion of elements: ")
for x in input:
for y in x:
print(y,end = " ")
print()
Output:

Size of a 2-D array
The length of an array can be determined using the len() method.
array_input = [[3,9],[0,3,7,10]]
print(len(array_input))
Output:
2
Python 2-D array Append
The elements can be appended to an array using the append() method. The element gets added to the end of the array.
from array import *
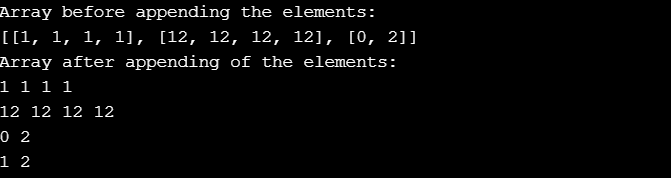
input = [[1,1,1,1], [12,12,12,12], [0,2]]
print("Array before appending the elements: ")
print(input)
input.append([1,2])
print("Array after appending of the elements: ")
for x in input:
for y in x:
print(y,end = " ")
print()
Output:
Slicing of a 2-D array in Python
Array slicing is used to access multiple values within an array.
Syntax:
<slice_array> = <array>[start:stop]
array1 = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6,7]]
#python array slice
array2 = array1[1:3] #index 1 to 2
print(array2)
array2 = array1[:1] #index 0 to 1
print(array2)
Output:

Conclusion
Thus, in this article, we have had an overview of Two Dimensional Arrays in Python and the basic functionalities involved with it.
References
- Python Arrays
- Python 2D Arrays
- Python Arrays Documentation


