🚀 Supercharge your YouTube channel's growth with AI.
Try YTGrowAI FreeSqlite “Create Table If Not Exists” Using Python

Hey, Python lovers (specifically programmers 😂 not snake lovers) here we are on a new topic of discussion and implementation:- “Sqlite – create table if not exists using Python”.
Now we all know about a very famous SQLite plugin sqlite3 which collaborates with the default Python environment. This helps us in making real-time applications and then connecting them to the database without using localhost or an online server.
We can call SQLite3 is a type of application that runs on a local machine without any config settings. So, to make things easier we are going to write a script that will check whether the table exists. If it does not exist it will automatically create one for us. This is just like making a smart tool. So, let us go for it!
Also read: Check If a Table Exists – Python SQLite3
Creating A Table If It Does Not Exist using Python SQLite3
Create a folder named Table Creation and then add the following code in a file in the same folder.
Code:
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.connect('database/school.db') # file path
# create a cursor object from the cursor class
cur = connection.cursor()
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE stud_data(
roll_no integer,
name text,
class integer,
division text
)''')
print("\nDatabase created successfully!!!")
# committing our connection
connection.commit()
# close our connection
connection.close()
Output:
Database created successfully!!!
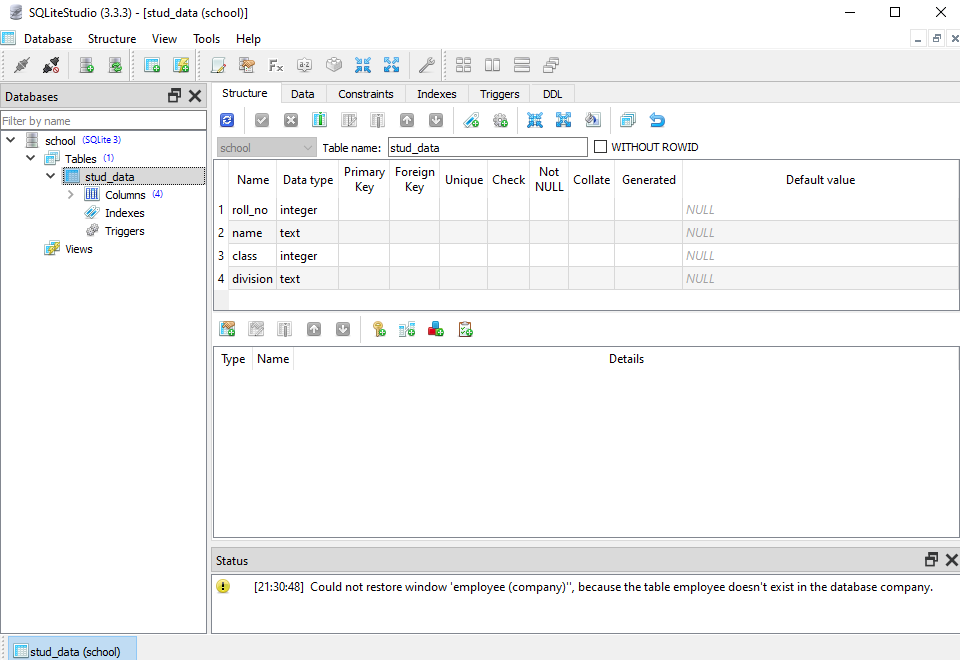
We created a school database that contains a student data table “stud_data”. The table has four columns: roll_no, name, class, and division. When we visualize it in SQLite studio, this looks like this:
Deleting the Table
Purposely we shall delete the table and then create our smart script.
Code to delete the table:
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.connect('database/school.db')
connection.execute("DROP TABLE stud_data")
print("Your table has been deleted!!!")
connection.close()
The DROP TABLE “table_name” query drops/deletes the table. Make sure to add the respective table name.
Output:
Your table has been deleted!!!
Complete Code to Create and Delete a Table
This section contains the major script that will check if the table exists or is not in the database. If the case happens then a new table with the same name and parameters is created.
Code:
import sqlite3
connection = sqlite3.connect('database/school.db')
cur = connection.cursor()
try:
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM stud_data")
# storing the data in a list
data_list = cur.fetchall()
print('Roll_Number' + '\t Name')
print('--------' + '\t\t-------------')
for item in items:
print(item[0] + ' | ' + item[1] + '\t' + item[2])
except sqlite3.OperationalError:
print("No such table: stud_data")
if(sqlite3.OperationalError): # if this error occurs
try:
print("Creating a new table: ")
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE stud_data(
roll_no integer,
name text,
class integer,
division text
)''')
print("New table created successfully!!!")
print("Here are the contents of the table: \n1: roll_no. \n2: name \n3: class \n4:division.")
except sqlite3.Error() as e:
print(e, " occured")
connection.commit()
connection.close()
Output:
No such table: stud_data
Creating a new table:
New table created successfully!!!
Here are the contents of the table:
1: roll_no.
2: name
3: class
4: division.
Explanation:
- We define two try blocks. The first one checks whether a table exists or not. If not the if condition jumps to the new try block and makes a new table for us.
- In the first try block: Using the SQLite query: “SELECT * FROM table_name” will try to fetch all the rows and columns from the table.
- If the table is absent try block throws sqlite.OperationalError. The except block handles it. The if() statement under it opens second try-except block.
- Then the second try statement accomplishes the task of creating a new table with the same parameters.
- The except block checks for any common error using sqlite.Error() method and handles it.
- The second part of the code just executes a query of creating a new table stud_data and inserting it into our database.
Wrapping up…
This is the way we can check whether a table exists in our SQLite database or not. It’s a recommendation to understand how the code works before implementing the solution. Thanks for reading.


