Functions in Python is a block of code with a name. We can call a function by its name and the code inside the function block will be executed. We can’t use reserved keywords as the function name. A function name must follow the Python identifiers definition rules.
Function Parameters
We can pass some data to functions to operate on, they are called function parameters. The function params are separated by a comma. We can have any number of parameters in a function.
Returning Data from a Function
A function can return data to the caller program. Unlike other popular programming languages, Python functions definition doesn’t specify the return type.
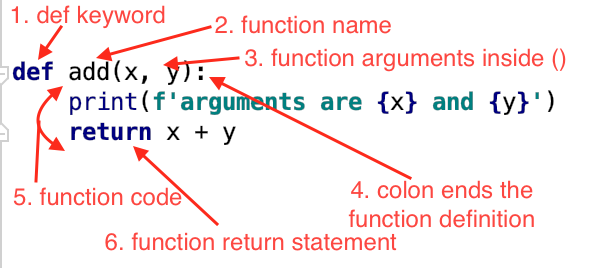
Define a Function in Python using the def keyword
We can define a function in Python using the def keyword. Let’s look at a couple of examples of a function in Python.
def hello():
print('Hello World')
def add(x, y):
print(f'arguments are {x} and {y}')
return x + y
Based on the above examples, we can define a function structure as this.
def function_name(arguments):
# code statements
Calling a Function in Python
We can call a function by its name. If the function accepts parameters, we have to pass them while calling the function.
hello()
sum = add(10, 5)
print(f'sum is {sum}')
We are calling hello() and add() functions that are defined by us. We are also calling the print() function which is one of the built-in functions in Python.
Python Function Types
There are two types of functions in Python.
- built-in functions: The functions provided by the Python language such as print(), len(), str(), etc.
- user-defined functions: The functions defined by us in a Python program.
Python Function Default Parameters
Python allows default values for the function parameters. If the caller doesn’t pass the parameter then the default value is used.
def hello(year=2019):
print(f'Hello World {year}')
hello(2020) # function parameter is passed
hello() # function parameter is not passed, so default value will be used
Output:
Hello World 2020
Hello World 2019
Multiple return statements inside a Function
A function can have multiple return statements. However, when one of the return statements is reached, the function execution terminates and the value is returned to the caller.
def odd_even_checker(i):
if i % 2 == 0:
return 'even'
else:
return 'odd'
print(odd_even_checker(20))
print(odd_even_checker(15))
Returning Multiple Values one by one using the yield keyword
Python function can return multiple values one by one. It’s implemented using the yield keyword. It’s useful when you want a function to return a large number of values and process them. We can split the returned values into multiple chunks using the yield statement. This type of function is also called a generator function.
def return_odd_ints(i):
x = 1
while x <= i:
yield x
x += 2
output = return_odd_ints(10)
for out in output:
print(out)
Output:
1
3
5
7
9
Variable Arguments in Python Function
Python allows three types of parameters in the function definition.
- Formal arguments: the ones we have seen in the examples so far.
- Variable Number of non-keyword arguments: for example, def add(*args)
- Variable Number of keyword arguments or named arguments: for example, def add(**kwargs)
Some important points about variable arguments in Python are:
- The arguments order should be formal arguments, *args, and **kwargs.
- It’s not mandatory to use variable parameter names such as args and kwargs. However, it’s the best practice to use them for better code readability.
- The args type is tuple. So we can pass a tuple to be mapped with the *args variable.
- The type of kwargs is dict. So we can pass a dictionary to be mapped with the **kwargs variable.
Here is a simple example of using variable arguments in a function.
def add(x, y, *args, **kwargs):
sum = x + y
for a in args:
sum += a
for k, v in kwargs.items():
sum += v
return sum
total = add(1, 2, *(3, 4), **{"k1": 5, "k2": 6})
print(total) # 21
Recursive Function in Python
When a function calls itself, it’s called a recursive function. This scenario is called recursion in programming.
You should be very careful when using recursion because there might be a chance that the function never terminates and goes into an infinite loop. Here is a simple example to print the Fibonacci series using recursion.
def fibonacci_numbers_at_index(count):
if count <= 1:
return count
else:
return fibonacci_numbers_at_index(count - 1) + fibonacci_numbers_at_index(count - 2)
count = 5
i = 1
while i <= count:
print(fibonacci_numbers_at_index(i))
i += 1
It’s good to know about recursion but most of the time you don’t need it in programming. You can perform the same thing using for-loop or while-loop.
Data Type of Function
Python functions are instances of the ‘function’ class. We can check this using type() function.
def foo():
pass
print(type(foo))
Output: <class ‘function’>
Function vs Method in Python
- Python function is part of the python script file in which it is defined whereas Methods are defined inside a class definition.
- We can call a function directly if it’s in the same module. If the function is defined in a different module, we can import the module and then call the function directly. We need a class or an object of the class to call the methods.
- Python function can access all the global variables whereas Python class methods can access global variables as well as class attributes and functions.
- Python functions data type is ‘function’ whereas Python methods data type is ‘method’.
Let’s look at a simple example of functions and methods in Python.
class Data:
def foo(self):
print('foo method')
def foo():
print('foo function')
# calling a function
foo()
# calling a method
d = Data()
d.foo()
# checking data types
print(type(foo))
print(type(d.foo))
Output:
foo function
foo method
<class 'function'>
<class 'method'>
Advantages of Python Functions
- Code reusability because we can call the same function multiple times
- Modular code since we can define different functions for different tasks
- Improves maintainability of the code
- Abstraction as the caller doesn’t need to know the function implementation
Anonymous Function in Python
Anonymous functions don’t have a name. We can define an anonymous function in Python using the lambda keyword.
def square(x):
return x * x
f_square = lambda x: x * x
print(square(10)) # 100
print(f_square(10)) # 100
Conclusion
Functions are an important part of a programming language. Python functions are defined using the def keyword. We can have a variable number of arguments in a Python function. Python also supports anonymous functions. They can return a single value or yield a number of values one by one.


