A comparison operator identifies the relationship between the operands and results into True or False.
One such basic yet important operator is not equal operator in Python.
It returns True if the values on either side of the operator are unequal i.e. it returns True when two variables of same type have different values, else it returns False.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| != | Not Equal operator, applicable and available in both Python 2 and Python 3. |
| <> | Not equal operator in Python 2, deprecated in Python version 3 and above. |
Python not equal Operator Syntax
operand1 != operand2
Example 1:
In the below snippet, 10 <> 20 results in a syntax error because it is deprecated in Python version 3 and above.
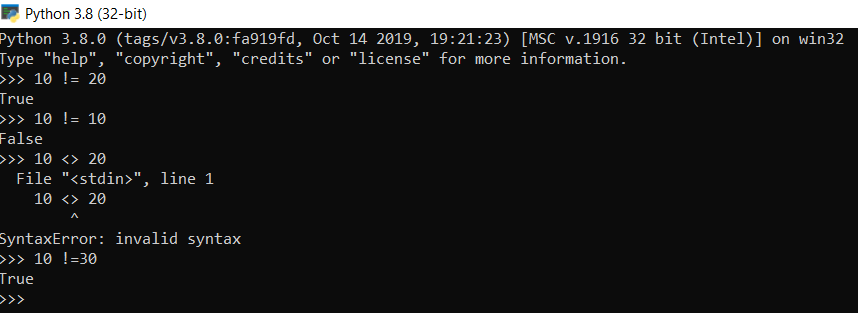
Example 2:

Output:

Python not equal Operator with custom object
Whenever we use the not equal operator, it calls __ne__(self, other) function. Thus, the user can define their own custom implementation for the objects and manipulate the natural or default outcome/output.
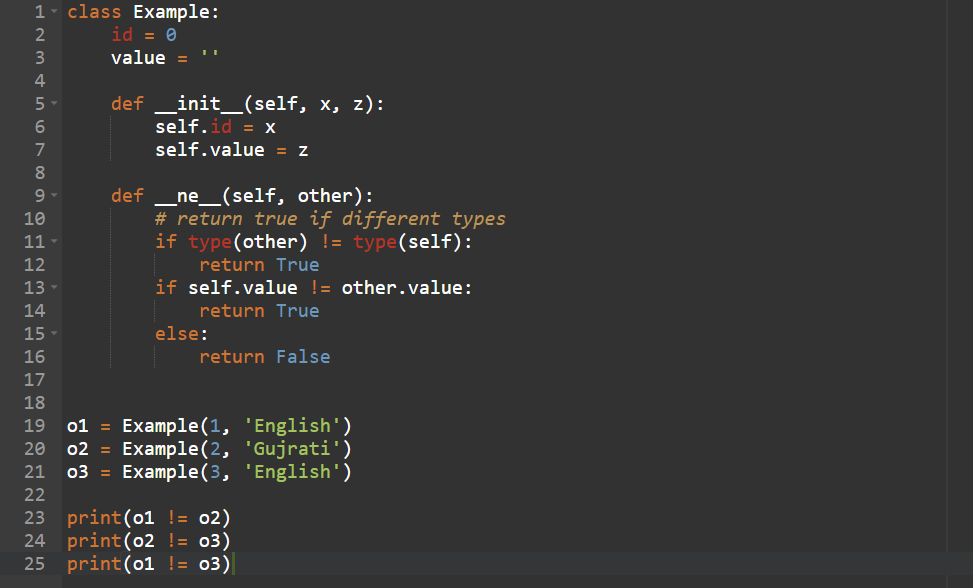
Output:

References
- Python not equal operator
- Python Comparison Operators
- Python Operators


