- Python while loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is False.
- The while loop is used when we don’t know the number of times the code block has to execute.
- We should take proper care in writing while loop condition if the condition never returns False, the while loop will go into the infinite loop.
- Every object in Python has a boolean value. If the value is 0 or None, then the boolean value is False. Otherwise, the boolean value is True.
- We can define an object boolean value by implementing
__bool__()function. - We use the reserved keyword – while – to implement the while loop in Python.
- We can terminate the while loop using the break statement.
- We can use continue statement inside while loop to skip the code block execution.
- Python supports nested while loops.
Python while Loop Syntax
while condition:
# while block code
Flow Diagram of while Loop
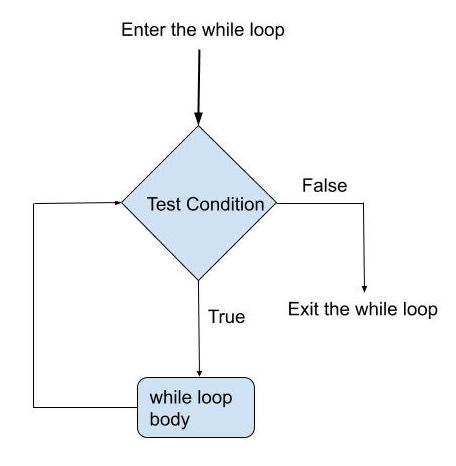
Python while Loop Examples
Let’s say we have to print a message given number of times. We can use while loop to write this utility function.
def print_msg(count, msg):
while count > 0:
print(msg)
count -= 1
print_msg(3, "Hello World")
Output:
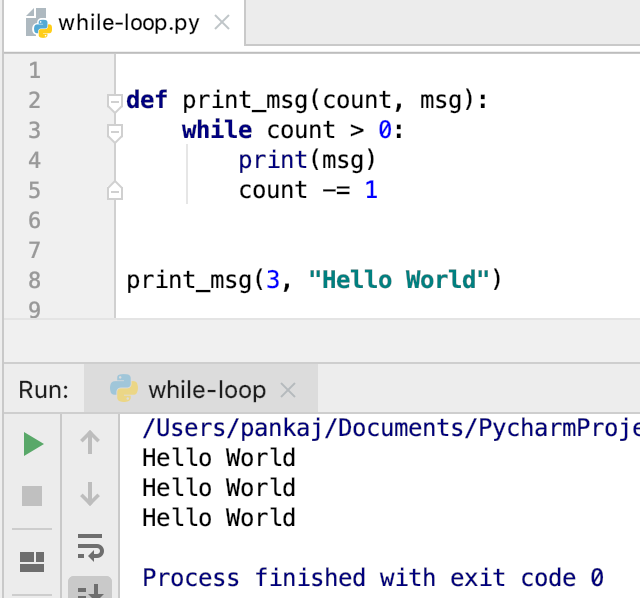
while Loop with break Statement
Sometimes we explicitly want to execute a code block indefinitely until the exit signal is received. We can implement this feature using “while True” block and break statement.
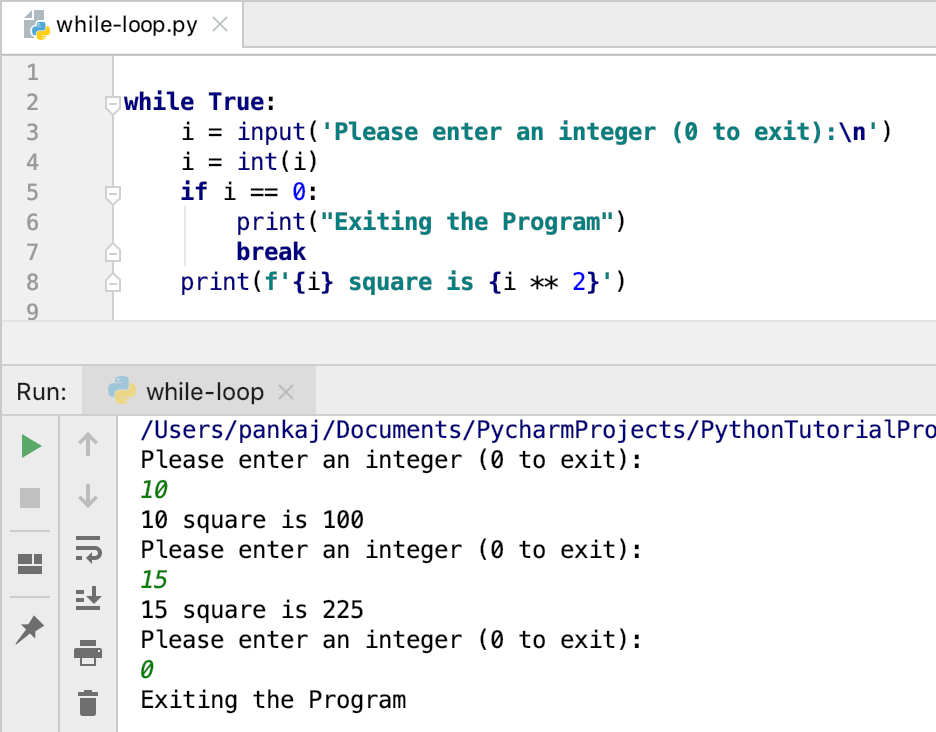
Here is an example of a utility script that takes the user input (integer) and prints its square value. The program terminates when the user enters 0.
while True:
i = input('Please enter an integer (0 to exit):\n')
i = int(i)
if i == 0:
print("Exiting the Program")
break
print(f'{i} square is {i ** 2}')
Here is the output of a sample run of this program.
Python while Loop with continue Statement
Let’s say we want the above script to work with positive numbers only. In that case, we can use continue statement to skip the execution when user enters a negative number.
while True:
i = input('Please enter an integer (0 to exit):\n')
i = int(i)
if i < 0:
print("The program works with Positive Integers only.")
continue
if i == 0:
print("Exiting the Program")
break
print(f'{i} square is {i ** 2}')
Output:
Please enter an integer (0 to exit):
5
5 square is 25
Please enter an integer (0 to exit):
-10
The program works with Positive Integers only.
Please enter an integer (0 to exit):
0
Exiting the Program
Python while Loop with else Statement
We can use else block with the while loop. The else block code gets executed when the while loop terminates normally i.e. the condition becomes False.
If the while loop terminates because of Error or break statement, the else block code is not executed.
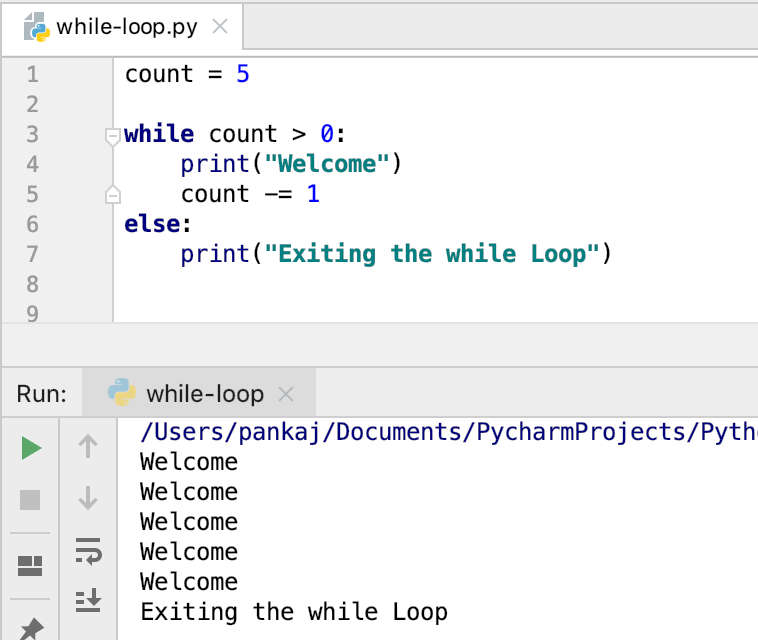
count = 5
while count > 0:
print("Welcome")
count -= 1
else:
print("Exiting the while Loop")
Output:
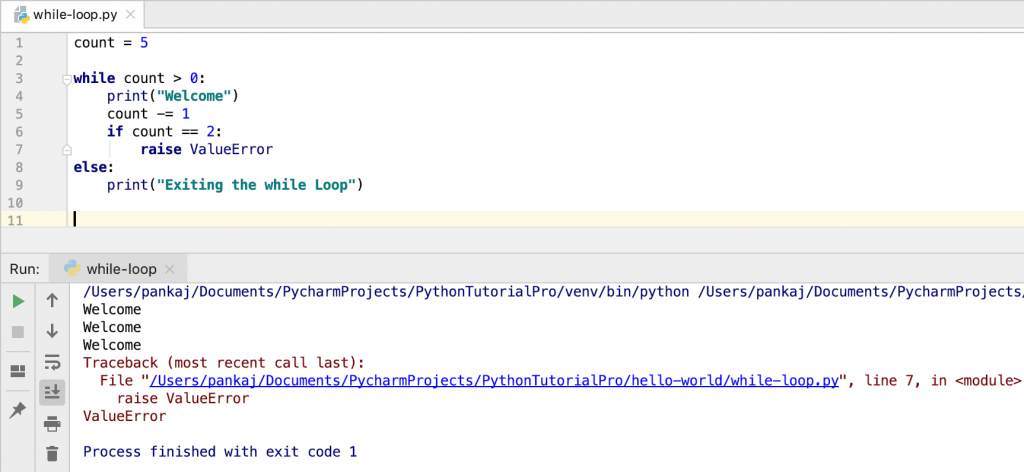
Let’s see what happens when the while loop terminates because of an error.
count = 5
while count > 0:
print("Welcome")
count -= 1
if count == 2:
raise ValueError
else:
print("Exiting the while Loop")
Output:
Welcome
Welcome
Welcome
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/pankaj/Documents/PycharmProjects/PythonTutorialPro/hello-world/while-loop.py", line 7, in <module>
raise ValueError
ValueError
Let’s change the program to break out of the while loop.
count = 5
while count > 0:
print("Welcome")
count -= 1
if count == 2:
break
else:
print("Exiting the while Loop")
Output:
Welcome
Welcome
Welcome
Nested while Loop Example
We can also have nested while loops. Here is an example of generating a list of tuples using nested while loops.
i = 3
j = 3
list_tuples = []
while i > 0:
while j > 0:
t = (i, j)
list_tuples.append(t)
j -= 1
j = 3
i -= 1
print(list_tuples)
Output: [(3, 3), (3, 2), (3, 1), (2, 3), (2, 2), (2, 1), (1, 3), (1, 2), (1, 1)]
Conclusion
Python while loop is used to run a code block for specific number of times. We can use break and continue statements with while loop. The else block with while loop gets executed when the while loop terminates normally. The while loop is also useful in running a script indefinitely in the infinite loop.


